
A Made IT project
http://www.made-it.com
info@made-it.com
 |
A Made IT projecthttp://www.made-it.com info@made-it.com |
General
The IEEE 1284 standard was approved in march 1994 as the Standard Signaling Method for a Bidirectional Parallel Peripheral Interface for Personal Computers. And is the first approved standard for parallel transmission on PCs. The idea was to create a standard that was backward compatible with the old Centronics standard. With the new standard higher speeds and greater distances are possible plus there is the capability also sending to the host (bidirectional).
The maximum speed that is allow over the new parallel bus is 2 MBps (16 Mbps). The cable length is determend by the mode that is used. Within the IEEE 1284 there are 5 different modes defined:
Compatibility mode
This one is compatible with all previous version of the parallel port. Data rates are possible up to 150 bytes per second @ 6 meter (20 ft) with an AB-cable or up to 150 kbps @ 10 meter (32.8 ft) with a CC-cable.
Nibble mode
This is a uni-directional interface. Only data transfers from periperal to host are possible. Data is send from the e.g. printer to the PC in a nibbles (4 bits). Combined with the Compatibility mode this is what Hewlett Packard calls "Bi-tronics".
For the Nibble-mode speeds of up to 50 kbps @ 6 meter (20 t) are possible. With a CC-cable this can be increased to up to 150 kbps @ 10 meter (32.6 ft).
Byte mode
Byte mode makes it possible to send data from the peripheral to the host in bytes (8 bits). Combined with the Compatibility mode you have a "Bidirectional port".
Speeds are possible up to 500 kbps @ 10 meter (32.8 ft) when CC-cables are used.
EPP mode
This is a mode in which data can be transfered from host to peripheral or vice versa, but not at the same time, so this is a half-duplex connection (mostly used by CD-ROMs, tape-drives, harddisks).
Speeds can range from 500 kbps to up to 2 Mbps @ 6 meter (20 ft) or 10 meter (32.8 ft) when CC-cables are used.
ECP mode
This is a mode in which data can be transfered from host to peripheral or vice versa, but not at the same time, so this is a half-duplex connection (mostly used by printers and scanners).
Speeds can range from 500 kbps to up to 1 Mbps @ 6 meter (20 ft) or 10 meter (32.8 ft) when CC-cables are used.
Every device can only be in one mode at a time. So the IEEE 1284 workgroup invented a way of determining which mode should be used with which device, that is called Negotiation. The Negotiation part doesn't affect older devices, but IEEE 1284 compliant devices can tell the host what they are and which mode to use.
Cables and Connectors
The IEEE defined three types of connectors and six types of cables. The type A connector is the parallel port connector (Sub-D25) found on most computers. The type B connector is what is usually called the Centronics connector. And there is a new connector that is called MDR36 and which is called type C. The pinning for the Centronics and Sub-D25 is not changed.
The different cables that are defined are:
| AMAM | Type A male to type A male |
|---|---|
| AMAF | Type A male to type A female |
| AB | Type A male to type B |
| AC | Type A male to type C |
| BC | Type B male to type C |
| CC | Type C male to type C |
Also the cable characteristics are defined:
Pinning Sub-D25 A-connector
| Male | Female |
|---|---|
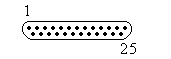 |
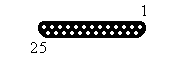 |
| Pin | Signal | Abbr. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data Strobe (low) | STROBE | Computer |
| 2 | Data Bit 1 (LSB) | D1 | Computer |
| 3 | Data Bit 2 | D2 | Computer |
| 4 | Data Bit 3 | D3 | Computer |
| 5 | Data Bit 4 | D4 | Computer |
| 6 | Data Bit 5 | D5 | Computer |
| 7 | Data Bit 6 | D6 | Computer |
| 8 | Data Bit 7 | D7 | Computer |
| 9 | Data Bit 8 (LSB) | D8 | Computer |
| 10 | Acknowledge (low) | ACK | Printer |
| 11 | Busy (high) | BUSY | Printer |
| 12 | Paper End (high) | PE | Printer |
| 13 | Select (high) | SEL | Printer |
| 14 | Auto Line Feed (low) | LF | Computer |
| 15 | Error (low) | ERROR | Printer |
| 16 | Initialize Printer (prime-low) | PRIME | Computer |
| 17 | Select Input (low) | SEL | Computer |
| 18 | Return/ground | GND | - |
| 19 | Return/ground | GND | - |
| 20 | Return/ground | GND | - |
| 21 | Return/ground | GND | - |
| 22 | Return/ground | GND | - |
| 23 | Return/ground | GND | - |
| 24 | Return/ground | GND | - |
| 25 | Return/ground | GND | - |
Pinning 36 pin Amphenol B-connector
| Male | Female |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| Pin | Signal | Abbr. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data Strobe (low) | STROBE | Computer |
| 2 | Data Bit 1 (LSB) | D1 | Computer |
| 3 | Data Bit 2 | D2 | Computer |
| 4 | Data Bit 3 | D3 | Computer |
| 5 | Data Bit 4 | D4 | Computer |
| 6 | Data Bit 5 | D5 | Computer |
| 7 | Data Bit 6 | D6 | Computer |
| 8 | Data Bit 7 | D7 | Computer |
| 9 | Data Bit 8 (LSB) | D8 | Computer |
| 10 | Acknowledge (low) | ACK | Printer |
| 11 | Busy (high) | BUSY | Printer |
| 12 | Paper End (high) | PE | Printer |
| 13 | Select (high) | SEL | Printer |
| 14 | Supply Ground | - | |
| 15 | Oscillator Transmit | Printer | |
| 16 | Logical Ground | - | |
| 17 | Chassis Ground | - | |
| 18 | +5 Vdc | +V | Printer |
| 19 | Return Data Strobe | - | |
| 20 | Return Data Bit 1 | - | |
| 21 | Return Data Bit 2 | - | |
| 22 | Return Data Bit 3 | - | |
| 23 | Return Data Bit 4 | - | |
| 24 | Return Data Bit 5 | - | |
| 25 | Return Data Bit 6 | - | |
| 26 | Return Data Bit 7 | - | |
| 27 | Return Data Bit 8 | - | |
| 28 | Return ACK | - | |
| 29 | Return BUSY | - | |
| 30 | Return Input Prime | - | |
| 31 | Input Prime (low) | Computer | |
| 32 | Fault (low) | FAULT | Printer |
| 33 | - | - | - |
| 34 | - | - | - |
| 35 | - | - | - |
| 36 | - | - | - |
Pinning MDR 36 pins C-connector
| Male | Female |
|---|---|
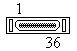 |
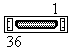 |
| Pin | Signal | Abbr. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Busy (high) | BUSY | Printer |
| 2 | Select (active high) | SEL | Printer |
| 3 | Acknowledge (active low) | ACK | Printer |
| 4 | Error (Fault- active low) | ERROR | Printer |
| 5 | Paper Error (active high | PE | Printer |
| 6 | Data Bit 0 (LSB) | D0 | Computer |
| 7 | Data Bit 1 | D1 | Computer/Printer |
| 8 | Data Bit 2 | D2 | Computer/Printer |
| 9 | Data Bit 3 | D3 | Computer/Printer |
| 10 | Data Bit 4 | D4 | Computer/Printer |
| 11 | Data Bit 5 | D5 | Computer/Printer |
| 12 | Data Bit 6 | D6 | Computer/Printer |
| 13 | Data Bit 7 (MSB) | D7 | Computer/Printer |
| 14 | Initial | INIT | |
| 15 | Data Strobe (low) | STROBE | Computer |
| 16 | Select Input (active low) | SI | |
| 17 | Auto Line Feed (active low) | ALF | |
| 18 | Host Logic High | HLH | Computer |
| 19 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 20 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 21 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 22 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 23 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 24 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 25 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 26 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 27 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 28 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 29 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 30 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 31 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 32 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 33 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 34 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 35 | Return/Ground | RGND | |
| 36 | Peripheral Logic High | PLH | Printer |
Functional Description
| STROBE | Active low pulse used to transfer data into the printer. | Pulse with must be between 0.5 and 500 microseconds for most printers. |
| ACK | Active low pulse indicates that data has been received and the printer is ready to accept more. | |
| BUSY | A high signal indicates that the printer cannot receive data. | |
| PE | A high signal indicates that the printer is out of paper (Paper End) | |
| SELECT OUT | A high signal indicates that the printer is on-line | |
| AUTO FEED | A low signal indicates to the printer that a line feed is required after each Carriage return. | This signal is used as a ground line by some manufacturers. |
| OSCXT | A 100-200 KHz signal used by true Centronics printers only. | |
| +5V | +5Vdc | Not provided by all manufacturers |
| PRIME | A low signal resets the printer to its power-up state and the printer buffer is cleared | |
| FAULT | A low signal indicates that the printer is in an off-line or error state | |
| LINE COUNT | Used by true Centronics printers only. | Most of the time not used |
| LINE COUNT | See 34 | |
| SELECT IN | A high signal indicates to the printer that a DC1/ DC3 code is valid. | This signal is used by a few manufacturers |
| Host Logic High | A high signal indicates that the host is alive (turned on). | Specific IEEE 1284 signal. |
| Peripheral Logic High | A high signal indicates that the peripheral (printer) is alive (turned on). | Specific IEEE 1284 signal. |